Border Guard (Poland)
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (March 2013) |
| Polish Border Guard Straż Graniczna | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Racing stripe | |
 Polish Border Guard Ensign | |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | 12 October 1990 |
| Preceding agencies |
|
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| National agency | Poland |
| Operations jurisdiction | Poland |
| Governing body | Border Guard General Headquarters (Poland) |
| Specialist jurisdictions |
|
| Operational structure | |
| Minister responsible | |
| Agency executive |
|
| Facilities | |
| Airplanes | PZL-104 Wilga, PZL M-28, PZL M-20 Mewa, Stemme ASP S15, Let L-410 Turbolet |
| Helicopters | PZL W-3 Sokół, Eurocopter EC135, PZL Kania, Robinson R44 |
| Website | |
| strazgraniczna | |
The Polish Border Guard (Polish: Straż Graniczna, also abbreviated as SG) is a state security agency tasked with patrolling the Polish border. It existed in the Second Republic era from 1928 to 1939 and was reestablished in the modern-day Third Republic in 1990, going into operation the following year. During the communist era lasting from 1945 to 1989, the role of the border guard was carried out by the Border Protection Troops (Wojska Ochrony Pogranicza).
History
[edit]1928–1939
[edit]The Straż Graniczna was founded in 1928. During the times of the Second Polish Republic, it was responsible for the northern, western and southern border of Poland (with Germany, the Free City of Danzig, the maritime border, Czechoslovakia and Romania). The eastern border, often raided by military bands supported by the Soviet Union, was under the jurisdiction of a separate, military formation (Border Protection Corps, Korpus Ochrony Pogranicza – KOP).
Responsibilities of Straż Graniczna included:
- prevention of illegal crossing of the land and sea border by people and goods (smuggling)
- ensuring safety and public order in the border area
- combating any threats to national security in the border area
The Border Guard was organized in a military style, with uniformed and armed agents. It was controlled by the Ministry of Treasury, Ministry of Internal Affairs, and Ministry of Military Affairs. The highest level of organizational structure of the agency was Main Headquarters (Komenda Główna), based in Warsaw. It was followed by Regional Inspectorates, Border Inspectorates, stations and posts. It carried out actions through patrols, manning border checkpoints, tracking, rouses and intelligence work. It had its own river and sea flotilla, intelligence academy, and the Main School of Border Guard (Centralna Szkoła Straży Granicznej), which was located firstly in Góra Kalwaria (until 1928), then in Rawa Ruska. The school had a department of training of guard dogs, also located in Rawa Ruska.
Each station of the agency was responsible for some 20 to 25 kilometers of the borderline. The stations oversaw posts of the first line and posts of the second line. In 1938, there were 129 stations of the Border Guard, 419 posts of the first line (these were located right along the border), and 212 posts of the second line (located in the interior of the country, right behind posts of the first line).
Regional inspectorates in 1939
[edit]- Mazovian Regional Inspectorate in Ciechanów,
- Pomeranian Regional Inspectorate in Bydgoszcz,
- Greater Poland Regional Inspectorate in Poznań,
- Silesian Regional Inspectorate in Katowice,
- Western Lesser Poland Regional Inspectorate in Kraków,
- Eastern Lesser Poland Regional Inspectorate in Lwów.
- Agency of the Customs Inspectorate of the Free City of Gdańsk.
In late 1938 and early 1939, following changes of borders of some Eastern European countries, the Border Guard took over protection of the boundary with Lithuania, while Border Defence Corps moved some of its units to the newly established border with Hungary. Furthermore, every station of the Border Guard was strengthened with a platoon of the Polish Land Forces.
Members of Straż Graniczna, under General Walerian Czuma, participated in the Second World War, fighting during the invasion of Poland together with Land Forces units.
1945–1989
[edit]During the period of the Polish People's Republic, the role of the border guards was carried out by the military formation of Border Protection Troops (Wojska Ochrony Pogranicza), being a part of the Polish People's Army and reporting directly to the Ministry of Interior, formerly under the Ministry of National Defense (from 1945 to 1949 and again from 1965 to 1970 and 1972), just as its 2nd Republic predecessors were assigned. After martial law, border battalions were reconstructed. Battalions were re-established in Sanok, Nowy Targ, Cieszyn, Racibórz, Prudnik, Zgorzelec, Gubin, Słubice and Chojna. The organization of battalions in Nowy Sącz, Lubań Śląski and Szczecin was stopped at the stage of the backbone commands. These were later disbanded.
1990 – present
[edit]Straż Graniczna has been reestablished in the Third Polish Republic as a civil, police-type service, with the act of 12 October 1990 and began operations on 16 May 1991. It considers itself the successor to the Second Polish Republic formations of the Straż Graniczna and Korpus Ochrony Pogranicza (plus the military heritage of the Wojska Ochrony Pogranicza of the People's Republic), and thus is one of the only police-styled forces to use military-style ranks (the Government Protection Bureau, Agencja Bezpieczeństwa Wewnętrznego and the Służba Więzienna also use them as well).
From 1 May 2004, the day Poland became a member of the European Union, Straż Graniczna has performed its responsibility to guard and protect both the Polish and EU borders.
Structure
[edit]- Border Guard General Headquarters (Warsaw)
- Warmińsko-Mazurski Border Guard Regional Unit (Kętrzyn)
- Podlaski Border Guard Regional Unit (Białystok)
- Bug Border Guard Regional Unit (Chełm)
- Bieszczady Border Guard Regional Unit (Przemyśl)
- Śląski Border Guard Regional Unit (Racibórz)
- Odra Border Guard Regional Unit (Krosno Odrzańskie)
- Sea Border Guard Regional Unit (Gdańsk)
- Vistula Border Guard Regional Unit (Warsaw)
- Carpathian Border Guard Regional Unit (Nowy Sącz).
Equipment
[edit]Border Wall
[edit]Firearms
[edit]- Mossberg 500
- Heckler & Koch MP5 9×19mm Parabellum
- HK 416[1]
- Glock 19 9×19mm Parabellum
- Glock 17 9×19mm Parabellum
- CZ P-10 C 9×19mm Parabellum[2]
- CZ Bren 2 PPS[3]
Utility vehicles
[edit]- Mitsubishi Pajero[4] [5]
- Citroen B E-C4[6]
- Peugeot Rifter[7]
- SEAT Ateca[8]
- Daewoo Musso[9][10] [11]
- Jeep Wrangler[12] [13]
- Renault Trafic[14]
- Toyota Hilux[15]
- Toyota Land Cruiser[16] [17]
Logistics vehicles
[edit]Aircraft
[edit]Helicopters
[edit]
Vessels
[edit]
- Griffon Hoverwork 2000TD
- Type SAR-1500
- SPORTIS S-7500
- Sportis S-7500K
- Type Mi-6
- Type SKS-40
- Type TM-623 OB CABIN
- Type TM-923 OB
- Type TM-1025 2IB CABIN
- Type IC 16 M III
- Type PARKER 1000 BALTIC
- Type Patrol 240 (Patrol 24 Baltic)
- Type SG-071[22]
- Type SG-301
Notable Border Guard commanders
[edit]Ranks
[edit]- Officers
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
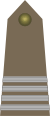
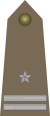
| Generał dywizji | Generał brygady | Pułkownik | Podpułkownik | Major | Kapitan | Porucznik | Podporucznik | Podchorąży
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Naval units |

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

|
Various | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
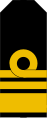
| Wiceadmirał | Kontradmirał | Komandor | Komandor porucznik | Komandor podporucznik | Kapitan marynarki | Porucznik marynarki | Podporucznik marynarki | Podchorąży
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Air department |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Various | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Generał dywizji | Generał brygady | Pułkownik | Podpułkownik | Major | Kapitan | Porucznik | Podporucznik | Podchorąży | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Enlisted
Gallery
[edit]-
PZL-104M
-
Kaper-2 Patrol Craft
-
SG-323 Patrol Craft
-
PZL W-3
-
SG-325 Patrol Craft
-
Quad vehicle of Border Guard
-
Motorboat of Border Guard
-
Land Rover Defender
-
EC 135 (P3H)
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ https://www.strazgraniczna.pl/pl/aktualnosci/12803,Nowe-dostawy-broni-dla-Strazy-Granicznej.html
- ^ "Sprzęt techniki specjalnej i optolektroniki".
- ^ https://bren3.czub.cz/
- ^ "Nowe samochody na granicę" (in Polish). 11 December 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ "Mitsubishi Pajero w Podlaskim OSG" (in Polish). 13 January 2015. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ "Straż Graniczna kupuje nowe auta" (in Polish). 30 July 2023. Retrieved 13 August 2024.
- ^ "Nowe pojazdy służbowe w Bieszczadzkim Oddziale SG" (in Polish). 24 January 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2024.
- ^ "Straż Graniczna kupuje nowe auta" (in Polish). 30 July 2023. Retrieved 13 August 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Militarypedia 2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Armiawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Nowy samochód w Sejnach" (in Polish). 15 January 2018. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ "Polska Straż Graniczna wybrała Jeepa Wranglera" (in Polish). 23 November 2020. Retrieved 13 August 2024.
- ^ "Pojazdy Straży Granicznej. Jakimi samochodami, motocyklami i quadami dysponują pogranicznicy?" (in Polish). 12 October 2021. Retrieved 13 August 2024.
- ^ "Nowe pojazdy służbowe w Bieszczadzkim Oddziale SG" (in Polish). 24 January 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2024.
- ^ "Kolejne Toyoty Hilux do Straży Granicznej" (in Polish). 3 June 2024. Retrieved 14 August 2024.
- ^ "Nowe Toyoty dla Straży Granicznej" (in Polish). 20 March 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ [hhttps://strazgraniczna.pl/pl/aktualnosci/11492,Nowe-toyoty-dla-Strazy-Granicznej.html "Nowe samochody na granicę"] (in Polish). 11 December 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ Zbiam (15 May 2019). "Volkswageny dla wojska". Wydawnictwo militarne ZBIAM (in Polish). Retrieved 23 September 2020.
- ^ "Seicento gotowy do służby w polskim wojsku". New-arch.rp.pl. Archived from the original on 16 April 2013. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- ^ "Statki powietrzne - Komenda Główna Straży Granicznej". Archived from the original on 13 January 2018.
- ^ "Statki powietrzne - Komenda Główna Straży Granicznej". Archived from the original on 13 January 2018.
- ^ "Jednostki pływające - Komenda Główna Straży Granicznej". Archived from the original on 13 January 2018.