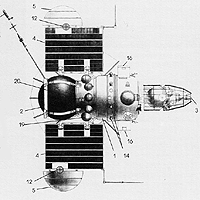
Venera 2MV-1 No.1
 | |
| Mission type | Venus lander |
|---|---|
| Operator | OKB-1 |
| Harvard designation | 1962 Alpha Pi 1[1] |
| COSPAR ID | 1962-040A |
| SATCAT no. | 372 |
| Mission duration | Launch failure |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | 2MV-1 |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
| Launch mass | 890 kilograms (1,960 lb) |
| Power | watts |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 25 August 1962, 02:18:45 UTC |
| Rocket | Molniya 8K78 s/n T103-12 |
| Launch site | Baikonur 1/5 |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | 28 August 1962 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth (achieved) Heliocentric (intended) |
| Eccentricity | 0.00403 |
| Perigee altitude | 168 kilometres (104 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 221 kilometres (137 mi) |
| Inclination | 64.9 degrees |
| Period | 88.71 minutes |
| Epoch | 25 August 1962 |
Venera 2MV-1 No.1,[2][1] also known as Sputnik 19 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme.
Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later.[3] It was the first of two Venera 2MV-1 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit.[1]
Launch
[edit]Venera 2MV-1 No.1 was launched at 02:18:45 UTC on 25 August 1962, atop a Molniya 8K78 carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome.[2] The first three stages of the rocket operated nominally, injecting the fourth stage and payload into a low Earth orbit. The fourth stage then coasted until one hour and fifty seconds after launch, when it fired its ullage motors in preparation for ignition. One of the ullage motors failed to fire, and when the main engine ignited for a four-minute burn to place the spacecraft into heliocentric orbit, the stage began to tumble out of control. Forty-five seconds later, its engine cut off, leaving the spacecraft stranded in Earth orbit.[4] It reentered the atmosphere on 28 August 1962, three days after it had been launched.[5][1]
Spacecraft designation
[edit]The designations Sputnik 23,[6] and later Sputnik 19 was used by the United States Naval Space Command to identify the spacecraft in its Satellite Situation Summary documents, since the Soviet Union did not release the internal designations of its spacecraft at that time, and had not assigned it an official name due to its failure to depart geocentric orbit.[7]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Krebs, Gunter. "Venera (2a), (2b) (2MV-1 #1, 2)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ^ a b McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ^ Wade, Mark. "Venera". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 11 December 2016. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ^ Wade, Mark. "Soyuz". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016. Retrieved 7 November 2019.
- ^ McDowell, Jonathan. "Satellite Catalog". Jonathan's Space Page. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ^ "Sputnik 19". NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ^ Robbins, Stuart J. (11 January 2006). "Soviet Craft - Sputnik". Journey Through The Galaxy. Archived from the original on 4 February 2009. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
