Tripeptide
Appearance
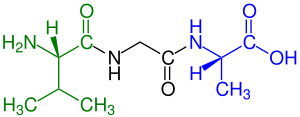
green marked amino end (L-Valine) and
blue marked carboxyl end (L-Alanine)
A tripeptide is a peptide derived from three amino acids joined by two or sometimes three peptide bonds.[1] As for proteins, the function of peptides is determined by the constituent amino acids and their sequence. In terms of scientific investigations, the dominant tripeptide is glutathione (γ-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine), which serves many roles in many forms of life.[2]
Examples
[edit]- Eisenin (pGlu-Gln-Ala-OH) is a peptide with immunological activity that is isolated from the Japanese marine alga, Eisenia bicyclis, which more commonly is known as Arame
- GHK-Cu (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) is a human copper binding peptide with wound healing and skin remodeling activity, which is used in anti-aging cosmetics and more commonly referred to as copper peptide
- Lactotripeptides (Ile-Pro-Pro and Val-Pro-Pro) found in milk products, act as ACE inhibitors
- Leupeptin (N-acetyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-argininal) is a protease inhibitor that also acts as an inhibitor of calpain
- Melanostatin (prolyl-leucyl-glycinamide) is a peptide hormone produced in the hypothalamus that inhibits the release of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
- Ophthalmic acid (L-γ-glutamyl-L-α-aminobutyryl-glycine) is an analogue of glutathione isolated from crystalline lens
- Norophthalmic acid (y-glutamyl-alanyl-glycine) is an analogue of glutathione (L-cysteine replaced by L-alanine) isolated from crystalline lens
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH, thyroliberin or protirelin) (L-pyroglutamyl-L-histidinyl-L-prolinamide) is a peptide hormone that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone and prolactin by the anterior pituitary
- ACV (δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-Cys-D-Val) is a key biosynthetic precursor to penicillin and cephalosporin.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M. (2005). Principles of Biochemistry (4th ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4339-6.
- ^ Guoyao Wu, Yun-Zhong Fang, Sheng Yang, Joanne R. Lupton, Nancy D. Turner (2004). "Glutathione Metabolism and its Implications for Health". Journal of Nutrition. 134 (3): 489–492. doi:10.1093/jn/134.3.489. PMID 14988435.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
